Mastering the Baseline Project Plan: Your Guide to Project Success
In the fast-paced world of project management, the baseline project plan stands as a vital blueprint for success, guiding teams from the initial conception to the final execution of projects. As the foundation upon which all project activities are built, understanding how to develop and maintain a strong baseline project plan can mean the difference between triumph and turmoil. This essential document not only provides a detailed roadmap for project tasks, timelines, and resource allocation but also serves as a critical tool for tracking progress and managing changes. In this guide, we will delve into the key components and best practices for creating an effective baseline project plan, equipping you with the knowledge to steer your projects toward successful completion.

Understanding the Baseline Project Plan
A baseline project plan is the cornerstone of successful project management. This section will explore what a baseline project plan entails and its key components, providing you with a solid foundation for your project management endeavors.
Defining a Baseline Project Plan
A baseline project plan is a snapshot of your project’s initial approved scope, schedule, and cost. It serves as a reference point against which all future progress is measured.
This crucial document is established at the beginning of a project, after thorough planning but before execution begins. It represents the project’s starting line and finish line, outlining the path between them.
The baseline acts as a contract between the project team and stakeholders, setting clear expectations for deliverables, timelines, and resource allocation. It’s the standard against which project performance is evaluated throughout its lifecycle.
Key Components of a Baseline Project Plan
A comprehensive baseline project plan consists of several essential elements that work together to provide a complete picture of the project’s trajectory.
The scope baseline defines the project’s boundaries, detailing what will and won’t be included. It typically encompasses the project charter, work breakdown structure (WBS), and scope statement.
The schedule baseline outlines the project timeline, including start and end dates for each task, milestones, and dependencies. This component is crucial for tracking progress and identifying potential delays.
The cost baseline represents the approved budget, broken down by project phases or deliverables. It’s used to monitor expenses and ensure the project remains financially on track.

Crafting Your Baseline Project Plan
Creating an effective baseline project plan requires careful consideration and a structured approach. This section will guide you through the process and highlight common pitfalls to avoid.
Steps to Develop an Effective Plan
Developing a robust baseline project plan involves a series of strategic steps that ensure all aspects of the project are considered and documented.
Define project objectives and scope clearly, ensuring alignment with stakeholder expectations.
Create a detailed work breakdown structure (WBS) to identify all necessary tasks and deliverables.
Estimate task durations and resource requirements, considering potential risks and constraints.
Develop a project schedule, incorporating task dependencies and critical path analysis.
Allocate resources and determine the budget, ensuring alignment with organizational capabilities.
Common Mistakes to Avoid
When creating a baseline project plan, be wary of these frequent errors that can undermine your project’s success from the start.
Underestimating complexity is a common pitfall. Always account for potential challenges and build in contingencies to your timeline and budget.
Failing to involve key stakeholders can lead to misaligned expectations and lack of buy-in. Ensure all relevant parties contribute to and approve the baseline plan.
Neglecting to document assumptions and constraints can cause issues later. Clearly state these factors in your plan to provide context for future decision-making.
Over-optimism in scheduling can set unrealistic expectations. Use historical data and expert judgment to create more accurate timelines.

Implementing and Monitoring
Once your baseline project plan is in place, the focus shifts to execution and tracking. This section will explore how to effectively monitor progress and make necessary adjustments to keep your project on course.
Tracking Progress Against Your Baseline
Regularly comparing actual performance to the baseline is crucial for maintaining project control and identifying potential issues early.
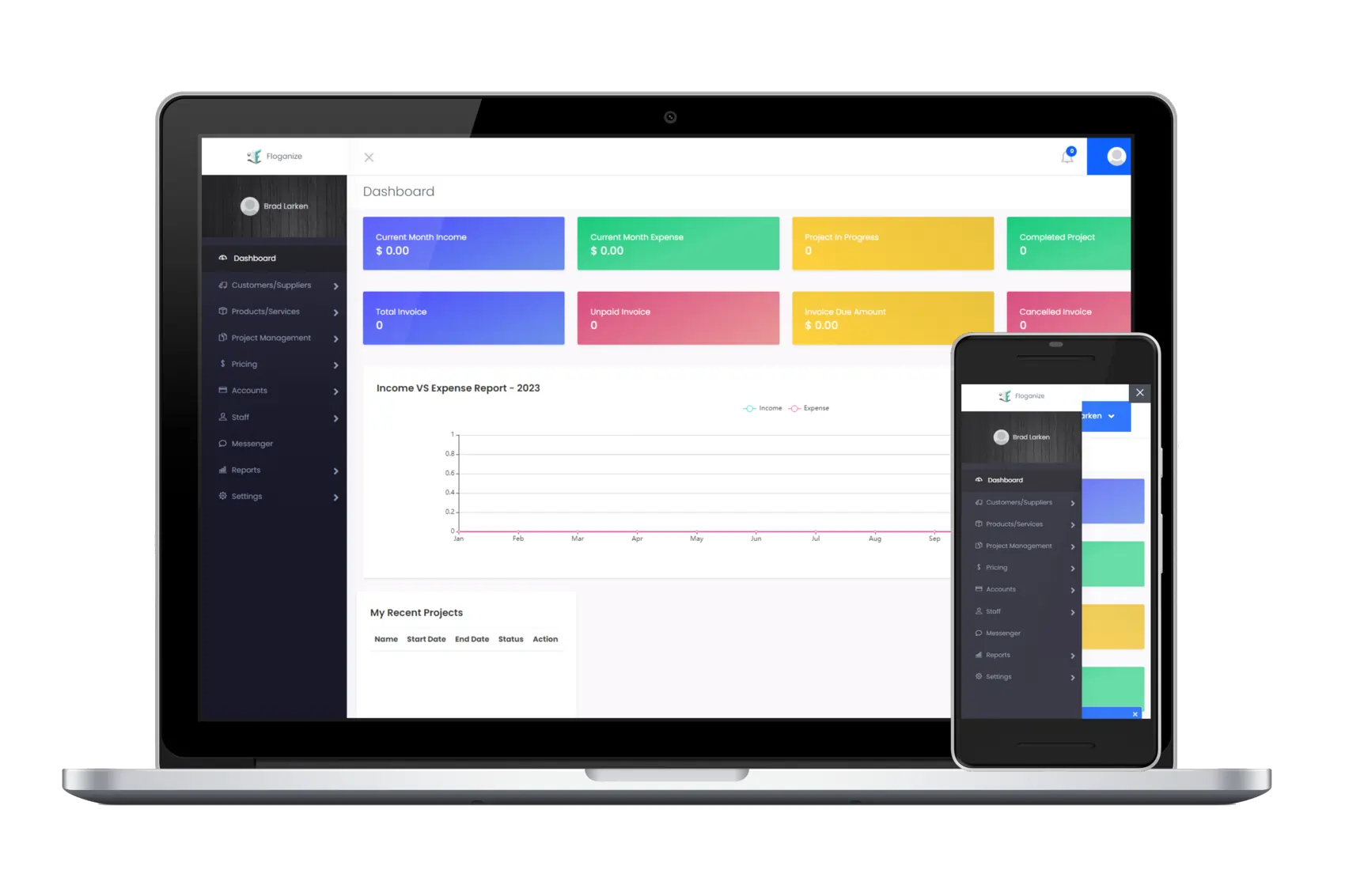
Use project management software to track task completion, resource utilization, and budget expenditure against the baseline. This provides real-time visibility into project status.
Conduct regular status meetings to review progress, discuss challenges, and update stakeholders. These meetings help ensure everyone remains aligned with the project goals.
Utilize earned value management (EVM) techniques to quantify project performance. EVM metrics like Schedule Performance Index (SPI) and Cost Performance Index (CPI) offer objective measures of progress.
Adjusting Plans for Success
While the baseline serves as a reference point, successful project management often requires flexibility and adaptability.
When significant deviations from the baseline occur, assess the impact on project objectives. Determine whether adjustments to the plan are necessary or if corrective actions can bring the project back on track.
If changes are required, follow a formal change control process. Document the reasons for changes, obtain necessary approvals, and update the baseline accordingly.
Regularly reassess risks and opportunities throughout the project lifecycle. This proactive approach allows you to mitigate potential issues and capitalize on favorable circumstances.